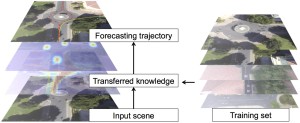
 Our paper “Knowledge Transfer for Scene-specific Motion Prediction”, by L. Ballan, F. Castaldo, A. Alahi, F. Palmieri and S. Savarese, has been accepted to ECCV 2016. A pre-print is available on arXiv.
Our paper “Knowledge Transfer for Scene-specific Motion Prediction”, by L. Ballan, F. Castaldo, A. Alahi, F. Palmieri and S. Savarese, has been accepted to ECCV 2016. A pre-print is available on arXiv.
When given a single frame of the video, humans can not only interpret the content of the scene, but also they are able to forecast the near future. This ability is mostly driven by their rich prior knowledge about the visual world, both in terms of (i) the dynamics of moving agents, as well as (ii) the semantic of the scene. We exploit the interplay between these two key elements to predict scene-specific motion patterns.
 Our paper “A Data-Driven Approach for Tag Refinement and Localization in Web Videos”, by myself, Marco Bertini, Giuseppe Serra, Alberto Del Bimbo, has been accepted for publication in Computer Vision and Image Understanding (CVIU) and is now available online.
Our paper “A Data-Driven Approach for Tag Refinement and Localization in Web Videos”, by myself, Marco Bertini, Giuseppe Serra, Alberto Del Bimbo, has been accepted for publication in Computer Vision and Image Understanding (CVIU) and is now available online.
Alberto Del Bimbo has been also invited to present our work at the Workshop on Large-Scale Video Search and Mining at CVPR 2015.
Estimating the relevance of a specific tag with respect to the visual content of a given image and video has become the key problem in order to have reliable and objective tags. With video tag localization is also required to index and access video content properly. In this paper, we present a data-driven approach for automatic video annotation by expanding the original tags through images retrieved from photo-sharing website, like Flickr, and search engines such as Google or Bing. Compared to previous approaches that require training classifiers for each tag, our approach has few parameters and permits open vocabulary.
 Our ICMR 2014 full paper “A Cross-media Model for Automatic Image Annotation” by Lamberto Ballan, Tiberio Uricchio, Lorenzo Seidenari and Alberto Del Bimbo has been accepted for oral presentation and it is now available online.
Our ICMR 2014 full paper “A Cross-media Model for Automatic Image Annotation” by Lamberto Ballan, Tiberio Uricchio, Lorenzo Seidenari and Alberto Del Bimbo has been accepted for oral presentation and it is now available online.
Automatic image annotation is still an important open problem in multimedia and computer vision. The success of media sharing websites has led to the availability of large collections of images tagged with human-provided labels. Many approaches previously proposed in the literature do not accurately capture the intricate dependencies between image content and annotations. We propose a learning procedure based on KCCA which finds a mapping between visual and textual words by projecting them into a latent meaning space. The learned mapping is then used to annotate new images using advanced nearest-neighbor voting methods.
Last friday I visited Fei-Fei Li’s Vision Lab at Stanford University and I had the pleasure of giving a very informal talk on our ongoing works on social media annotation. The slides of the talk are available online.
 Our ICME 2013 paper “An evaluation of nearest-neighbor methods for tag refinement” by Tiberio Uricchio, Lamberto Ballan, Marco Bertini and Alberto Del Bimbo is now available online.
Our ICME 2013 paper “An evaluation of nearest-neighbor methods for tag refinement” by Tiberio Uricchio, Lamberto Ballan, Marco Bertini and Alberto Del Bimbo is now available online.
The success of media sharing and social networks has led to the availability of extremely large quantities of images that are tagged by users. The need of methods to manage efficiently and effectively the combination of media and metadata poses significant challenges. In particular, automatic image annotation of social images has become an important research topic for the multimedia community. In this paper we propose and thoroughly evaluate the use of nearest-neighbor methods for tag refinement and we report an extensive and rigorous evaluation using two standard large-scale datasets.
 Our paper “Knowledge Transfer for Scene-specific Motion Prediction”, by L. Ballan, F. Castaldo, A. Alahi, F. Palmieri and S. Savarese, has been accepted to ECCV 2016. A pre-print is available on arXiv.
Our paper “Knowledge Transfer for Scene-specific Motion Prediction”, by L. Ballan, F. Castaldo, A. Alahi, F. Palmieri and S. Savarese, has been accepted to ECCV 2016. A pre-print is available on arXiv.





