Our paper “Automatic Image Annotation via Label Transfer in the Semantic Space”, by T. Uricchio, myself, L. Seidenari and A. Del Bimbo, has been accepted for publication in Pattern Recognition and is now available online. It is an extended version of our KCCA-based tag propagation model presented in our ICMR’14 paper, containing more experiments and a novel tag denoising procedure.
A few days later, our paper “Learning without Prejudice: Avoiding Bias in Webly-Supervised Action Recognition” has been also accepted for publication in Computer Vision and Image Understanding (CVIU) and is now available online. Here we present a (fully) webly-supervised model for action recognition in videos. This is a joint work with F. Tombari and C. Rupprecht from TUM (Germany).
 I am co-organizing a special issue for the Computer Vision and Image Understanding journal on “Computer Vision and the Web”, together with Shih-Fu Chang (Columbia University), Gang Hua (Microsoft Research Asia), Thomas Mensink (Univ. of Amsterdam), Greg Mori (Simon Fraser Univ.) and Rahul Sukthankar (Google Research). You can see all the details on the call for papers.
I am co-organizing a special issue for the Computer Vision and Image Understanding journal on “Computer Vision and the Web”, together with Shih-Fu Chang (Columbia University), Gang Hua (Microsoft Research Asia), Thomas Mensink (Univ. of Amsterdam), Greg Mori (Simon Fraser Univ.) and Rahul Sukthankar (Google Research). You can see all the details on the call for papers.
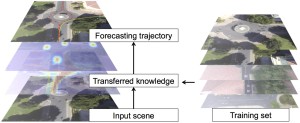 Our paper “Knowledge Transfer for Scene-specific Motion Prediction”, by L. Ballan, F. Castaldo, A. Alahi, F. Palmieri and S. Savarese, has been accepted to ECCV 2016. A pre-print is available on arXiv.
Our paper “Knowledge Transfer for Scene-specific Motion Prediction”, by L. Ballan, F. Castaldo, A. Alahi, F. Palmieri and S. Savarese, has been accepted to ECCV 2016. A pre-print is available on arXiv.
When given a single frame of the video, humans can not only interpret the content of the scene, but also they are able to forecast the near future. This ability is mostly driven by their rich prior knowledge about the visual world, both in terms of (i) the dynamics of moving agents, as well as (ii) the semantic of the scene. We exploit the interplay between these two key elements to predict scene-specific motion patterns.
 Everything you wanted to know about image tagging, tag refinement and social image retrieval. Our paper has been (finally) accepted to ACM Computing Surveys! This is a titanic effort, by Xirong Li, Tiberio Uricchio, myself, Marco Bertini, Cees Snoek and Alberto Del Bimbo, to structure the growing literature in the field, understand the ingredients of the main works, clarify their connections and difference, and recognize their merits and limitations.
Everything you wanted to know about image tagging, tag refinement and social image retrieval. Our paper has been (finally) accepted to ACM Computing Surveys! This is a titanic effort, by Xirong Li, Tiberio Uricchio, myself, Marco Bertini, Cees Snoek and Alberto Del Bimbo, to structure the growing literature in the field, understand the ingredients of the main works, clarify their connections and difference, and recognize their merits and limitations.
A pre-print is available on arXiv and the source code is on GitHub.
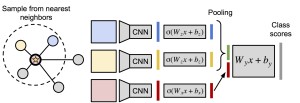 Our paper “Love Thy Neighbors: Image Annotation by Exploiting Image Metadata”, by J. Johnson*, L. Ballan* and L. Fei-Fei (* equal contribution), has been accepted to ICCV 2015. A pre-print is now available on arXiv.
Our paper “Love Thy Neighbors: Image Annotation by Exploiting Image Metadata”, by J. Johnson*, L. Ballan* and L. Fei-Fei (* equal contribution), has been accepted to ICCV 2015. A pre-print is now available on arXiv.
Some images that are difficult to recognize on their own may become more clear in the context of a neighborhood of related images with similar social-network metadata. We build on this intuition to improve multilabel image annotation. Our model uses image metadata nonparametrically to generate neighborhoods of related images using Jaccard similarities, then uses a deep neural network to blend visual information from the image and its neighbors.
 Our paper “A Data-Driven Approach for Tag Refinement and Localization in Web Videos”, by myself, Marco Bertini, Giuseppe Serra, Alberto Del Bimbo, has been accepted for publication in Computer Vision and Image Understanding (CVIU) and is now available online.
Our paper “A Data-Driven Approach for Tag Refinement and Localization in Web Videos”, by myself, Marco Bertini, Giuseppe Serra, Alberto Del Bimbo, has been accepted for publication in Computer Vision and Image Understanding (CVIU) and is now available online.
Alberto Del Bimbo has been also invited to present our work at the Workshop on Large-Scale Video Search and Mining at CVPR 2015.
Estimating the relevance of a specific tag with respect to the visual content of a given image and video has become the key problem in order to have reliable and objective tags. With video tag localization is also required to index and access video content properly. In this paper, we present a data-driven approach for automatic video annotation by expanding the original tags through images retrieved from photo-sharing website, like Flickr, and search engines such as Google or Bing. Compared to previous approaches that require training classifiers for each tag, our approach has few parameters and permits open vocabulary.
 Our ICMR 2014 full paper “A Cross-media Model for Automatic Image Annotation” by Lamberto Ballan, Tiberio Uricchio, Lorenzo Seidenari and Alberto Del Bimbo has been accepted for oral presentation and it is now available online.
Our ICMR 2014 full paper “A Cross-media Model for Automatic Image Annotation” by Lamberto Ballan, Tiberio Uricchio, Lorenzo Seidenari and Alberto Del Bimbo has been accepted for oral presentation and it is now available online.
Automatic image annotation is still an important open problem in multimedia and computer vision. The success of media sharing websites has led to the availability of large collections of images tagged with human-provided labels. Many approaches previously proposed in the literature do not accurately capture the intricate dependencies between image content and annotations. We propose a learning procedure based on KCCA which finds a mapping between visual and textual words by projecting them into a latent meaning space. The learned mapping is then used to annotate new images using advanced nearest-neighbor voting methods.
 Our ICME 2013 paper “An evaluation of nearest-neighbor methods for tag refinement” by Tiberio Uricchio, Lamberto Ballan, Marco Bertini and Alberto Del Bimbo is now available online.
Our ICME 2013 paper “An evaluation of nearest-neighbor methods for tag refinement” by Tiberio Uricchio, Lamberto Ballan, Marco Bertini and Alberto Del Bimbo is now available online.
The success of media sharing and social networks has led to the availability of extremely large quantities of images that are tagged by users. The need of methods to manage efficiently and effectively the combination of media and metadata poses significant challenges. In particular, automatic image annotation of social images has become an important research topic for the multimedia community. In this paper we propose and thoroughly evaluate the use of nearest-neighbor methods for tag refinement and we report an extensive and rigorous evaluation using two standard large-scale datasets.
 Our paper “Copy-Move Forgery Detection and Localization by Means of Robust Clustering with J-Linkage” by I. Amerini, L. Ballan, R. Caldelli, A. Del Bimbo, L. Del Tongo, and G. Serra, has been accepted for publication by the Signal Processing: Image Communication journal (pdf, link); more info on this page.
Our paper “Copy-Move Forgery Detection and Localization by Means of Robust Clustering with J-Linkage” by I. Amerini, L. Ballan, R. Caldelli, A. Del Bimbo, L. Del Tongo, and G. Serra, has been accepted for publication by the Signal Processing: Image Communication journal (pdf, link); more info on this page.
Understanding if a digital image is authentic or not, is a key purpose of image forensics. There are several different tampering attacks but, surely, one of the most common and immediate one is copy-move. A recent and effective approach for detecting copy-move forgeries is to use local visual features such as SIFT. Often, this procedure could be unsatisfactory, in particular in those cases in which the copied patch contains pixels that are spatially distant, and when the pasted area is near to the original source. In such cases, a better estimation of the cloned area is necessary in order to obtain an accurate forgery localization. We present a novel approach for copy-move forgery detection and localization based on J-Linkage which performs a robust clustering in the space of the geometric transformation.
 Our paper entitled “Context-Dependent Logo Matching and Recognition” – by H. Sahbi, L. Ballan, G. Serra and A. Del Bimbo – has been accepted for publication in the IEEE Transactions on Image Processing (pdf, link). Part of this work was conducted while me and G. Serra were visiting scholars at Telecom ParisTech (in spring 2010).
Our paper entitled “Context-Dependent Logo Matching and Recognition” – by H. Sahbi, L. Ballan, G. Serra and A. Del Bimbo – has been accepted for publication in the IEEE Transactions on Image Processing (pdf, link). Part of this work was conducted while me and G. Serra were visiting scholars at Telecom ParisTech (in spring 2010).
We contribute through this paper to the design of a novel variational framework able to match and recognize multiple instances of multiple reference logos in image archives. Reference logos as well as test images, are seen as constellations of local features (interest points, regions, etc.) and matched by minimizing an energy function mixing (i) a fidelity term that measures the quality of feature matching (ii) a neighborhood criterion which captures feature co-occurrence/geometry and (iii) a regularization term that controls the smoothness of the matching solution. We also introduce a detection/recognition procedure and we study its theoretical consistency. We show the validity of our method through extensive experiments on the novel challenging MICC-Logos dataset overtaking, by 20%, baseline as well as state-of-the-art matching/recognition procedures. We present also results on another public dataset, the FlickrLogos-27 image collection, to demonstrate the generality of our method.












